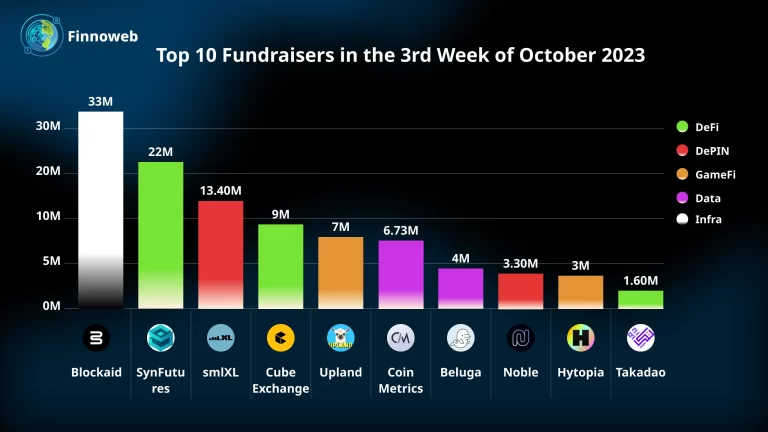
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing various industries worldwide. But what is it, and how does it work? Let’s delve into the world of blockchain, its history, types, advantages, disadvantages, smart contracts, decentralization, cryptocurrencies, and its future impact on society.
What is Blockchain and How Does It Work?
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. These transactions are stored in “blocks,” which are linked together, creating a “chain.” Each block contains a list of transactions and a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block.
Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, meaning there is no central authority or intermediary. When a new transaction occurs, it is verified by network participants through consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). Once someone validates it, they add the transaction to the ledger and it becomes a permanent part of the blockchain.
The History of Blockchain and Its Evolution
Blockchain technology began with the launch of Bitcoin in 2009 by an anonymous person or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto. The creators designed Bitcoin’s blockchain as a secure and transparent way to record and verify transactions.
Over time, blockchain evolved beyond cryptocurrencies. Ethereum, introduced in 2015, allowed for the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). This expansion marked the beginning of blockchain’s broader applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology
Advantages
1. Security: The cryptographic nature of blockchain ensures that data is secure and tamper-proof.
2. Transparency: Transactions are visible to all network participants, enhancing trust.
3. Decentralization: Eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
4. Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity.
Disadvantages
1. Scalability: Some blockchains face challenges in handling a high volume of transactions quickly.
2. Energy Consumption: Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms are energy-intensive.
3. Regulatory Concerns: The anonymity of blockchain transactions can raise regulatory issues.
There are already solutions to these disadvantages, like Proof Of Stake consensus, which is much more energy efficient, and has faster transactions and there are other organizations that have managed to use the computational power for more productive things like training ML models and more such.
Different Types of Blockchains
Blockchain comes in several types:
1. Public Blockchains
Public blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to anyone and are maintained by a decentralized network. Anyone can participate, transact, and view the ledger.
2. Private Blockchains
Private blockchains are restricted to specific users or organizations. They offer increased privacy and control but sacrifice some decentralization.
3. Hybrid Blockchain
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of both public and private blockchains. They offer the benefits of decentralization while allowing for controlled access.
Smart Contracts and Their Role in Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute when predefined conditions are met. Smart contracts are a key innovation of blockchain, enabling the automation of processes in a trustless and secure manner. They have applications in legal agreements, supply chain management, and more.
Decentralization and Its Impact on Industries
Decentralization is a fundamental aspect of blockchain technology that has the potential to disrupt various industries, such as finance and supply chain management.
Finance
In finance, blockchain can streamline transactions, reduce costs, and enhance security. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are emerging, providing financial services without intermediaries.
Supply Chain
Blockchain’s transparency and traceability make it ideal for supply chain management. It allows consumers to track the origins of products, ensuring quality and ethical sourcing.
Cryptocurrencies and How They Work on Blockchain
Cryptocurrencies are digital assets that operate on blockchain technology. They are used for various purposes, including as a medium of exchange, a store of value, and a unit of account. The most famous cryptocurrency is Bitcoin, but thousands of others exist, each with its unique features and uses.
Cryptocurrencies operate on blockchain through transactions, where ownership is transferred from one address to another. These transactions are validated by miners or validators, depending on the blockchain’s consensus mechanism.
Exploring the Transformative Power of Blockchain in Various Sectors
Blockchain technology is poised to usher in a new era of innovation across a myriad of industries, promising to reshape the way we live and interact with the world. Let’s delve into these potential impacts in greater detail:
1. Healthcare Transformation
In the healthcare sector, blockchain offers a game-changing solution to issues related to patient data management. Providing a secure, decentralized ledger for patient records, guarantees enhanced security, privacy, and interoperability. In practical terms, this means that medical professionals can access a patient’s complete medical history securely and in real-time, even across different healthcare providers or regions. Furthermore, it facilitates streamlined administrative processes, enabling healthcare facilities to focus on delivering quality care instead of grappling with complex data management.
2. Reinventing Democracy
One of the most exciting prospects of blockchain technology is its potential to revolutionize voting systems. Through blockchain, secure, transparent, and tamper-proof online voting platforms can be developed. These platforms have the potential to bolster democratic processes by ensuring fair and verifiable elections, while also enhancing voter accessibility. A blockchain-based voting system can significantly reduce the likelihood of electoral fraud, increase voter participation, and instill greater confidence in the democratic process.
3. Safeguarding Intellectual Property
Blockchain technology presents a robust solution for safeguarding intellectual property rights. By securely recording ownership and provenance on an immutable ledger, creators, and innovators can protect their work from plagiarism and unauthorized usage. This will enable artists, authors, inventors, and content creators to receive fair compensation for their creations, fostering a more equitable ecosystem for intellectual property management.
4. A Decentralized Energy Landscape
The energy sector is on the cusp of a significant transformation due to blockchain. This technology can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing individuals and businesses to directly exchange excess energy without the need for intermediaries. In essence, consumers can become producers, contributing to a more sustainable and decentralized energy grid. This shift reduces reliance on centralized utilities and enables a more efficient distribution of energy resources, contributing to a greener, more sustainable future.
5. Streamlined Identity Verification
Identity verification is another realm where blockchain can simplify and fortify processes. By securely storing identity information on a blockchain, individuals can have greater control over their data. This means that users can selectively share their information with trusted parties, reducing the risk of identity theft. Moreover, this innovation also holds the potential to simplify cumbersome verification processes, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements in the financial sector, thereby streamlining transactions and reducing friction in various areas of life.
Conclusion
The future of blockchain is undeniably promising and expansive, with the potential to positively impact various facets of our lives. From ensuring the security of our data in healthcare to redefining the way we participate in democracy, safeguard intellectual property, manage energy resources, and verify our identities, the applications of blockchain are vast and far-reaching. The journey toward a blockchain-powered society is filled with endless possibilities, and as it unfolds, it promises to reshape the way we live, work, and engage with the world around us.

Follow Finnoweb news for more such.